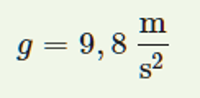In physicsPhysics is the scientific study of matter, energy, space, and time, and of the relations between them., we try to understand the laws of nature. The path to explaining the phenomenon is often as follows:
- Physicists observe phenomena closely in nature or in the laboratory.
- They formulate several explanations (hypotheses) to try to explain the observed phenomenon. This is done with the help of observation and past discoveries.
- They plan a test experiment to check which of the proposed explanations is correct.
- They perform a test experiment.
- They present (graph, picture, snapshot, etc.) and analyse the measurements.
Explanatory hypotheses can become theories after lengthy and thorough testing. Hypotheses that provide descriptive generalisations can become laws.
Watch the clip below and answer the questions.
What research question did Galileo ask?
What was his first explanation (hypothesis)?
What did the experiment show?
The video shows Galileo conducting an experiment.
His question is which spheres will reach the ground faster.
He thinks of Aristoteles and puts forward the first explanation – the heavier one will reach the ground first.
The experiment shows that both spheres hit the ground at the same time.
Why did both spheres fall at the same time?
Do you want to know more?
The spheres are falling freely. They are only acted on by the force of gravity, or the gravitational force that the Earth exerts on all the objects in its surroundings. The gravitational force is always directed towards the centre of the Earth.
Gravitational acceleration acts on the spheres. The gravitational acceleration at the surface of the Earth is the same for all objects. We label it g.